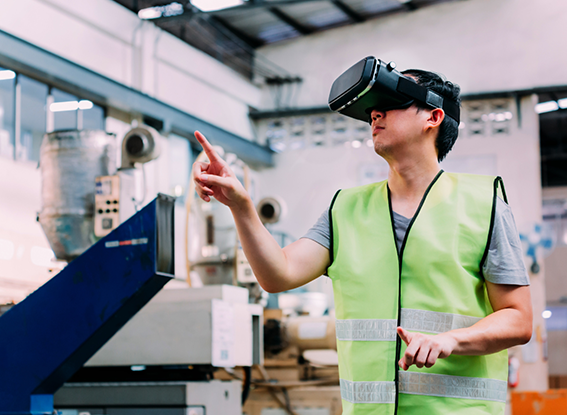
Join the Legacy of Innovation.
40 Years in the Making.
2025 marks the 40th anniversary of MD&M West, and we are committed to celebrating the manufacturing achievements of the past 40 years while continuing to act as a hub of imagination, connection, and learning for the betterment of the world in the next 40 years and beyond. Join us in Anaheim and celebrate the legacy of manufacturing excellence at one of the largest and most influential b2b advanced manufacturing trade shows in the world.
Your Stories of Manufacturing Excellence
Chapman University
As The Shah Family Endowed Chair in Innovativeness and a professor teaching manufacturing at Chapman University along

MeKo Manufacturing e.K.
MeKo proudly reflects on over 30 years of excellence in laser material processing. Founded in 1991 by Dr. Meyer-Kobbe, MeKo became a pioneer in

INCOE
Since 1958, INCOE’s Hot Runner Systems have been the heart of the injection molding process, managing, and controlling Melt Logistics® inside the

Zollner
With a global presence in Europe, America, Asia and Africa, the company can react flexibly to geopolitical challenges, fulfill local market

Inventus Power
As MD&M West has been highlighting year after year, the medical device industry is ever-changing, with new technology helping to advance life-saving solutions.

Zeus Industrial Products, Inc.
Founded by Frank P. Tourville, Sr. in 1966 and built upon the principle that "there is no 'good enough' in true craftsmanship," Zeus has

RPK Group
Founded in 1974 by 19 entrepreneurs in Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain, RPK Group has grown into a dynamic global organization with manufacturing facilities

UpNano
Founded in 2018 as a spin-off from TU Wien, UpNano combined cutting-edge research with entrepreneurial vision from the minds of CTO Peter

Absolute Haitian
Absolute Haitian’s journey As a legacy exhibitor with MD&M West – specifically Plastec West – we congratulate the show on 40 years of connecting

Ray Products Co., Inc
Ray Products has been shaping the future of plastics manufacturing since 1949. As a family-owned business now in its third generation, we’ve

Heraeus Medevio
Throughout our history, we have evolved from a component manufacturer to a full-service contract design, development, and manufacturing partner to

Uson
For over 60 years, Uson has been at the forefront of leak testing technology, delivering innovative solutions across industries like medical device

Elos Medtech
In 2023, Elos Medtech celebrated 100 years in the industry - a century filled with groundbreaking achievements and strategic expansions that

New England Wire Technologies
From the earliest days of our founding in 1898, New England Wire is proud to have developed some of the most innovative capabilities and wire and

Wytech
For 50 years, Wytech and its sister company, Mountain Manufacturing Technologies, have supplied over 1 billion parts to the medical device

Janman Precision
For 40 years, Janman Precision has been at the forefront of precision manufacturing, consistently pushing the boundaries of what's.

Westfall Technik
At Westfall, we remain focused on redefining what’s possible in plastics manufacturing and contributing to the innovation and

IGS GeboJagema
At IGS GeboJagema, we consider it an enormous privilege to work in the healthcare industry. By excelling in our craft, we have the opportunity to

Millar
From the very start, Millar has been at the forefront of sensor innovation, developing products and technologies that revolutionize how clinicians

LaserStar Technologies
LaserStar Technologies is a U.S. manufacturer of laser products and has engineered, designed, and built laser systems and solutions for use in

BioInteractions Limited
BioInteractions, a leading UK biomaterial technology company, began with a simple mission: to improve patient healthcare through smarter and safer medical

Nien-Yi Industrial Corp.
With over 25 years of experience in custom cable manufacturing, we've grown from our initial focus on wire and cable production to offering

Freeman Schwabe Machinery
Freeman Schwabe®, located in Cincinnati, Ohio, has a rich history in die cutting, evolving over 90 years-and still going strong.

Tessy Plastics Corp.
Tessy was founded by Henry Beck in 1973 in Elbridge, NY. Tessy is still owned and operated by the Beck family today.

SEKISUI Voltek
Founded in 1969, SEKISUI Voltek has been pioneering advanced foam solutions for over 55 years, empowering industries to create products that

Furukawa Techno Material Co., Ltd.
40 years ago, by 1985, Furukawa already had a vacuum furnace and actively melted Nitinol. From the beginning we have been a rare supplier

SEKISUI KYDEX
The SEKISUI KYDEX story began 60 years ago, in 1965 when KYDEX® 100 was invented at Rohm & Haas Co. At its outset, this high-impact, fire-rated, and

marco Systems Analysis and Development LLC
At marco System Analysis and Development, we are leaders in creating high-performance dispensing systems that are essential

Avantor’s NuSil
For 45 years, Avantor’s NuSil brand has set the global standard in medical- and space-grade silicones, advancing purity and quality while redefining

Minitubes
Founded nearly a century ago in Grenoble, Minitubes is a family-owned company. A mid-sized enterprise (ETI) specializing in small-diameter, high-precision

Crescent Industries Inc.
Established in 1988, Belton Technology Group is an ISO 13485, 16949, 9001, 14001, QS9000 certified and UL listed components and full turnkey contract

Paragon Medical
Located in Warsaw, Indiana, in the old Warsaw Steel Building, Paragon Medical was incorporated on June 14, 1991 and began designing and
Crescent Industries Inc.
With over 78 years of experience, Crescent Industries has proven to be a reliable leader in mold building and injection molding.

AMADA WELD TECH INC.
Since our founding in 1948, Amada Weld Tech has been committed to the design and manufacture of innovative and reliable equipment and systems for

CIRCOR
Innovating for a Century: Zenith Pumps’ Journey to Excellence in Medical Device Production Since our founding in 1926, Zenith Pumps has been at

Technipaq
Celebrating 40 Years of Technipaq: A Journey from Start-Up to Industry Leader In 1984, Technipaq was founded with a vision to provide innovative,
ADMEDES GmbH
ADMEDES is part of the medtech industry since 1996 and renowned for its cutting-edge technologies and innovative solutions.

VitalPath
VitalPath is made up of three well-established medical device contract manufacturing companies with more than 45 years of combined experience as

Accumold
Our founders discovered there was a growing need to manufacture small and micro injection molded components that went well-beyond the available

Precipart
At Precipart, we Engineer Possible. From contributing to the world’s most iconic innovations—such as gramophone needles, Polaroid cameras, and the

Primo Medical Group
In 1953, Primo Tallarida started a machining business in a chicken coop in a Massachusetts town. He named it Stoughton Tool & Die. From there he

MORETTO USA CORP.
From vision to reality: shaping the future of the plastics industry! Moretto proudly stands as a beacon of innovation and excellence in the plastics

Medbio / Caplugs
Since our founding in 2004, Medbio has grown into a leader in full-service medical manufacturing, offering customers in-house cleanroom molding,

UFP MedTech
Founded in 1963, UFP MedTech is a designer and custom manufacturer of comprehensive solutions for medical devices, sterile packaging, and other

Altech Corporation
As an advanced supplier of disconnect switches, miniature circuit breakers, terminal blocks and enclosures, Altech has been in the forefront of

START International
Since 1981, START International has been solving customer's application needs with products serving manufacturing industries.

Nihon Dento Kougyo Co. Ltd.
Nihon Dento Kougyo Co., Ltd. was founded in 1958 and will be 67 years in 2025. Our company, which has led the manufacturing industry in Japan with its

Vernay
With over 75 years of expertise, Vernay shares MD&M West’s commitment to innovation, collaboration, and advancing the MedTech

Bernd Richter GmbH
Bernd Richter GmbH develops and produces cable and connector systems for the medical, defense and industrial markets.

Fort Wayne Metals
Founded in 1970 with a vision to redefine the role of materials in advancing healthcare, we’ve spent over five decades innovating wire-based

PSN Labs
Our story began in the early 1990s with Dr. Paul Koch, founder of the Plastics Engineering program at Penn State Behrend. Combining years of

Roehm America LLC
CYROLITE® compounds by Röhm are the world’s leading acrylic polymer developed especially for use in the Medical Device Industry. The brand was

ADDEV Materials
Founded in 2006, ADDEV Materials is a high growth company that delivers value-added products and services for the health care, medical device,

Promex
Promex Industries has shaped the future of microelectronic contract manufacturing for medical and biotech devices over the last five decades.
Eagle Stainless
In 1982, Eagle Stainless Tube & Fabrication began in a small boiler room in Franklin, MA, with a commitment to delivering the highest-quality

Actuonix Motion Devices, Inc.
Founded in 2004 as Firgelli Technologies, Actuonix Motion Devices has become a leader in the design and manufacturing of compact linear motion

Integer
Integer is one of the largest medical contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) in the world, offering

Renishaw, Inc.
At Renishaw, we have spent over 50 years engineering change. Our company was first established in 1973, by Sir David McMurtry and John Deer. Renishaw’s

Precision Associates, Inc.
Precision Associates, Inc. (PAI) is proud to celebrate its 70th year as a leading manufacturer of high-performance, precision-molded rubber

ISPG Inc.
For nearly 40 years ISPG has been providing specialty components to exacting specification to the global medical device and pharmaceutical

Moldex3D
CoreTech System Co., Ltd. (Moldex3D) was founded in 1995 and is proudly approaching its 30th anniversary. For three decades, we have been at

MAJiK Medical Solutions Pvt. Ltd.
We are glad to know that MD&M West’s 40-year anniversary coincides with full completion of MAJiK’s new state-of the art 100,000 SFT facility for

Command Medical Products LLC
Having attended the MD&M shows since 1998, I continue to be amazed by the scale of the event and the incredible array of medtech manufacturing

JW Winco
JW Winco started in the basement of the Winkler family basement, 45 years ago. JW Winco is a leader in standard parts - with locations in the USA,

Starlim North America Corp.
Starlim has been a pioneer in the field of silicone injection molding for over 40 years. Starlim’s international group of companies continues to

MTD Micro Molding
MTD Micro Molding’s evolution from a micro tooling company to a trailblazer in medical micro molding is a testament to relentless innovation,

KMM Group, Ltd.
KMM Group's origins lie in two family-owned precision manufacturing businesses. KV Incorporated (KVI), founded in 1977 by

PUNCH INDUSTRY USA INC.
PUNCH INDUSTRY USA, Itasca, Illinois, is proud to have earned the trust of American manufacturers, tool and die makers, plastic injection molders, metal

ProPlate
Celebrating ProPlate’s Legacy of Innovation and Excellence at MD&M West’s 40-Year Anniversary ProPlate is proud to join MD&M West in celebrating

RBP Chemical Technology
RBP Chemical Technology: 70 Years of Innovation and Excellence In 1954, RBP Chemical Technology began as "Research for Better Printing,"
GCM
GCM, with over 40 years of experience, operates from various worldwide locations including Union City CA, Chicago, Atlanta, and Dongguan China.

Cincinnati Test Systems
Cincinnati Test Systems, Inc (CTS) based out of the Greater Cincinnati area is a leader in supplying leak test systems that conducts non-destructive

Plitek
PLITEK®: From Start-Up to Industry Leader in Precision Die Cutting and Converting As MD&M West celebrates 40 years of innovation, we at PLITEK®

Pro-Tech Design & Manufacturing
PRO-TECH Design is celebrating our own anniversary - 45 years! - in 2025. The company was founded in 1980 by Pam McMaster in her family

Qosina
As Qosina celebrates its 45th anniversary in 2025, I’m reminded of the early days of MD&M West, which I’ve exhibited at since its very first event in 1985.

Pivot International
Founded in 1972, Pivot International is a globally recognized leader in product design, development, and electronic manufacturing.

ComplianceQuest
Since its inception, ComplianceQuest has rapidly grown into a global leader in cloud-based quality, compliance, and safety management

Dordan Manufacturing
Dordan celebrates its golden birthday today, turning 62 and custom thermoforming since 1962. Dordan is a third generation, family owned

HASCO America Inc.
HASCO America, Inc. is part of HASCO, a worldwide corporation that just celebrated its 100-year anniversary! I've been with HASCO America for over 20

Norman Noble, Inc.
From humble beginnings in a Cleveland, Ohio garage in 1946, Norman Noble, Inc. has grown into a powerhouse of precision contract manufacturing,

Fralock
Fralock has a rich history of innovation and excellence in the medical device industry, where we have become a trusted partner for advanced materials

Andrews Cooper
For 25 years, Andrews Cooper has been setting the bar higher than the rest. For our team, “Engineering the Impossible in “HardTech”

Innovize
Founded in 1958 as GML, Innovize has grown from a small manufacturer to a leader in the medical device manufacturing industry. In 2009,

Micro-Tek Corporation
Founded in 1965 by George Rogers, Micro-Tek Corporation, originally known as the Miniature Insulated Wire Company, was incorporated under its

PHS West
Started in 1995, PHS West is celebrating our 30 year anniversary in 2025! From our humble beginnings stemming from an idea our founder had to create a

Vision Engineering Inc.
Vision Engineering was founded in 1958 by Rob Freeman, a toolmaker and innovator with a vision to enhance precision and efficiency in

Gitchia Institute of Global Certification
As the CEO of ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE & MEDICAL DEVICES SOLUTION (SMC-PRIVATE) LIMITED, I am excited to share our journey at the intersection

Sono-Tek Corporation
MD&M Wests's 40th year celebration of manufacturing excellence coincides with Sono-Tek Corporation's 50th year celebration of medical

HUI Manufacturing
HUI was founded in 1933. We started as a small appliance store in a small town in Wisconsin. Fast-forward over ninety years and we have transformed

MD+DI
For more than 40 years now, MD&M and its official media brand, Medical Device + Diagnostic Industry (MD+DI), have been critical resources for

Plastics Today
When the Medical Design & Manufacturing (MD&M) Exposition debuted in 1985, plastics were already well integrated in the medical technology
Our MD&M West Story
Inception & Growth
For 40 years, this renowned advanced manufacturing expo has had a history of growth, innovation, and community. From its inception in 1985 by Canon Communications LLC, our advanced manufacturing trade show’s infancy began in the Disneyland Hotel in Anaheim, CA as a small B2B event. It brought local manufacturers specializing in medical device components, manufacturing equipment, and innovative materials together to supply purchasing companies with the latest innovations needed to advance their manufacturing initiatives.
Through the late eighties and early nineties, MD&M West grew in size and reputation. The show relocated to the Anaheim Convention Center to accommodate the growing number of exhibitors and attendees. With this increase in scale, MD&M West continued to advance its scope in manufacturing. Each year brought more companies from a variety of manufacturing areas to support the changing landscape and needs of medtech and manufacturing. Educational conferences and networking opportunities were introduced in the following years to give attendees and exhibitors more tools to connect and learn, allowing them to grow their network and adapt to the rapid trends and developments in the industry.
UBM Canon & International Exposure
The growing popularity of MD&M West in the early 2000s brought more opportunities for expansion, and Canon Communications was acquired by UBM (United Business Media), leading to the rebranding of the trade show under UBM Canon. UBM leveraged its reputation and resources to develop the trade show into not just a regional event, but an international one with more industry-leading manufacturers showcasing their cutting-edge technologies from countries like China, Japan, India, Germany, and the UK.
Informa Markets & The Show Today
In 2018, UBM was acquired by Informa Markets, which took over the management of MD&M West. This transition brought new opportunities for the trade show, with Informa Markets enhancing the event's digital presence and introducing more interactive and immersive experiences for attendees. Over the past four decades, MD&M West has developed into one of the largest and most influential trade shows in the manufacturing industry, regularly attracting tens of thousands of professionals and featuring thousands of exhibitors from around the world. The show has consistently adapted to the changing landscape of medical technology and beyond, from the early days of mechanical components to the current focus on smart devices, artificial intelligence, and sustainable manufacturing practices.
The 40-Year Evolution of Advanced Manufacturing
1980s
The 1980s marked a significant transformation in the manufacturing industry with the widespread adoption of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems. These technologies revolutionized the way products were designed and manufactured, allowing for greater precision and efficiency. Robotics and automation began to play a crucial role on the factory floor, leading to improved productivity and consistency in production. Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing emerged, emphasizing the importance of reducing waste and optimizing inventory management. Additionally, advancements in materials science, particularly in composites and alloys, enabled the development of stronger, lighter, and more durable products.
Notable Achievements and Devices:
- Introduction of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM).
- Emergence of robotics and automation in manufacturing lines.
- Development of Just-in-Time (JIT) manufacturing.
- Advancements in materials science, particularly in composites and alloys.
- Introduction of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI).
- Development of minimally invasive surgical instruments.
- Growth in the use of electronic medical records (EMRs).
- Significant improvements in prosthetics and implantable devices, such as pacemakers.
1990s
The 1990s saw the rise of lean manufacturing principles, which focused on waste reduction and continuous improvement. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems became integral to managing complex business processes, providing better integration and control over production, supply chains, and finance. The use of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines grew, offering enhanced precision and flexibility in manufacturing operations. This decade also witnessed the early stages of 3D printing technology, primarily used for rapid prototyping, which laid the groundwork for future advancements in additive manufacturing. Globalization significantly impacted the industry, leading to more complex supply chains and the outsourcing of manufacturing to lower-cost regions.
Notable Achievements and Devices:
- Rise of lean manufacturing principles.
- Development of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems.
- Increasing use of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines.
- Early advancements in 3D printing technology for prototyping.
- Introduction of laparoscopic surgery.
- Development of stents for cardiovascular treatments.
- Growth in home medical devices, such as glucometers and blood pressure monitors.
- Increased focus on biocompatible materials for implants and prosthetics.
2000s
In the 2000s, the manufacturing industry embraced Six Sigma methodologies to improve quality and reduce defects. The expansion of globalization continued, creating more intricate supply chains and driving companies to outsource manufacturing processes. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) began to gain traction beyond prototyping, finding applications in low-volume production. The implementation of advanced robotics and automation, including the introduction of collaborative robots (cobots), enhanced productivity and worker safety. Sustainable manufacturing practices also started to gain attention, as companies sought to reduce their environmental impact.
Notable Achievements and Devices:
- Adoption of Six Sigma methodologies.
- Expansion of globalization and complex supply chains.
- Growth in additive manufacturing (3D printing).
- Implementation of advanced robotics and collaborative robots (cobots).
- Development of advanced imaging technologies, such as PET/CT scanners.
- Introduction of drug-eluting stents.
- Growth in telemedicine and remote monitoring devices.
- Advancements in genetic testing and personalized medicine.
2010s
The 2010s were characterized by the emergence of Industry 4.0, which integrated the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, and cyber-physical systems into manufacturing processes. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning played a crucial role in predictive maintenance, quality control, and optimizing production. Additive manufacturing technologies matured, with 3D printing being widely adopted for both prototyping and production, including metal additive manufacturing. Sustainability became a central focus, with manufacturers implementing green practices to reduce waste and energy consumption. Digital twins and advanced simulation tools enabled real-time monitoring and optimization of manufacturing systems.
Notable Achievements and Devices:
- Emergence of Industry 4.0, integrating IoT, big data, and cyber-physical systems.
- Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning for predictive maintenance.
- Widespread adoption of 3D printing for prototyping and production.
- Increased focus on sustainability and green manufacturing practices.
- Growth in wearable health technology, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches.
- Development of advanced robotic surgery systems, like the da Vinci Surgical System.
- Advancements in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
- Increased use of AI and machine learning in diagnostics and treatment planning.
2020s
The 2020s are witnessing the further integration of AI, machine learning, and IoT in creating smart factories and autonomous manufacturing systems. Advanced materials, such as nanomaterials and bio-based composites, are being developed to enhance product performance and sustainability. Digital twins are becoming more prevalent, allowing for real-time simulation and optimization of manufacturing processes. Blockchain technology is being increasingly used for supply chain transparency and security, ensuring the authenticity and traceability of products. The industry continues to focus on sustainability, adopting circular economy principles and striving for zero-waste processes.
Notable Achievements and Devices:
- Further integration of AI, machine learning, and IoT for smart factories.
- Development of advanced materials, including nanomaterials and bio-based composites.
- Expansion of digital twins for real-time simulation and optimization.
- Increased use of blockchain technology for supply chain transparency and security.
- Advancements in personalized and precision medicine driven by AI and big data.
- Growth in telehealth and remote patient monitoring, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Development of advanced implantable devices and bioelectronics.
- Continued innovation in minimally invasive surgery and advanced imaging technologies.
2030s & Beyond
Looking ahead to the 2030s and beyond, the manufacturing industry is expected to fully realize the potential of Industry 5.0, where humans and machines work collaboratively in highly adaptive and flexible environments. Quantum computing will revolutionize complex simulations and optimization problems, driving further advancements in manufacturing processes. Sustainable manufacturing practices will become the norm, with a strong emphasis on circular economy principles and zero-waste operations. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) will be widely integrated into training and operational support, enhancing worker skills and efficiency. The industry will continue to innovate, pushing the boundaries of technology and sustainability.
Anticipated Achievements and Devices:
- Full realization of Industry 5.0 with human-machine collaboration.
- Widespread use of quantum computing for complex simulations and optimization.
- Continued advancements in sustainable manufacturing with circular economy principles.
- Integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) for training and operational support.
- Breakthroughs in biotechnology and regenerative medicine, such as organ regeneration.
- Development of fully autonomous surgical robots and AI-driven diagnostic systems.
- Growth in personalized medicine with real-time health monitoring and predictive analytics.
- Continued innovation in nanomedicine and targeted drug delivery systems.